
Your browser does not support the audio element.

Listen to a recorded reading of this page:.Take a ten question quiz about this page.Next, the cell wall "pinches" off in the middle forming two separate cells. Then the duplicate strands of DNA move to opposite sides of the cell. First the DNA replicates and the cell grows to twice its normal size. Simple organisms such as bacteria undergo a type of cell division called binary fission. The splitting of the cells is called cytokinesis or cell cleavage. The two new cells, or daughter cells, are formed. The cell walls then pinch off and split down the middle. Telophase - During telophase the cell forms two nuclear membranes around each set of chromosomes and the chromosomes uncoil.Anaphase - During anaphase the chromosomes separate and move to opposite sides of the cell.Metaphase - During metaphase the chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell.Prophase - During this phase the chromatin condenses into chromosomes and the nuclear membrane and nucleolus break down.When a cell gets the signal that it is to duplicate, it will enter the first state of mitosis called the "prophase". The genetic material is duplicated during the interphase stage of the cell. The "normal" state of a cell is called the "interphase".
Prophase in mitosis full#
The full process, or cycle, of mitosis is described in more detail below.Įxamples of cells that are produced through mitosis include cells in the human body for the skin, blood, and muscles.Ĭells go through different phases called the cell cycle.
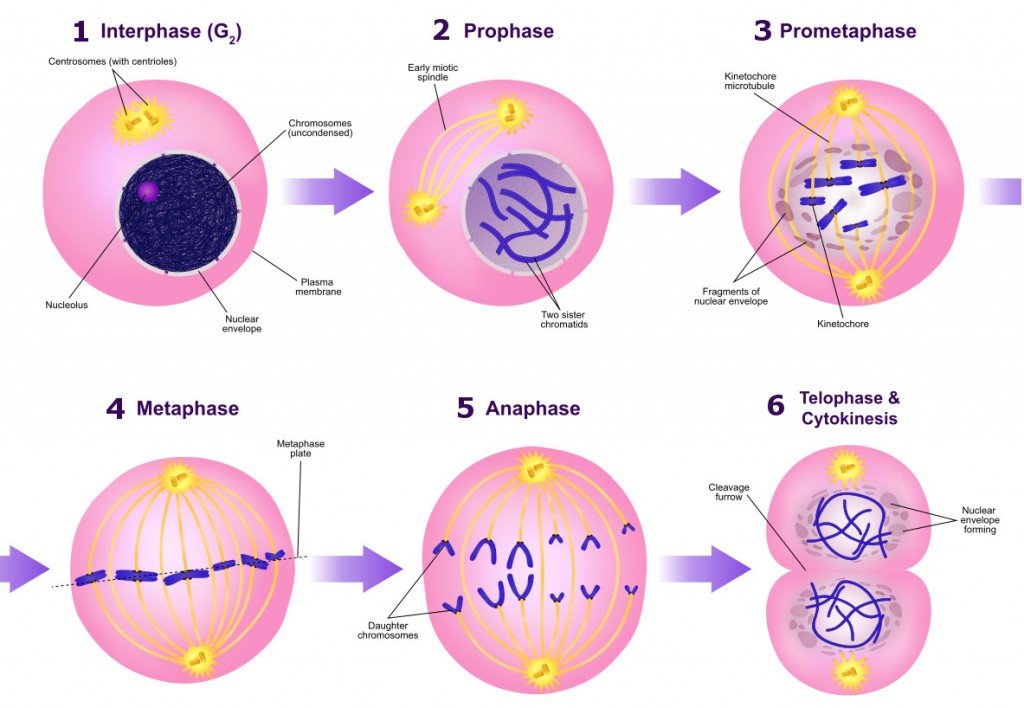
The original cell is called the mother cell and the two new cells are called daughter cells. The two new cells have the same DNA, functions, and genetic code. Mitosis is used when a cell needs to be replicated into exact copies of itself. More complex organisms gain new cells by either mitosis or meiosis. Binary fission is used by simple organisms like bacteria. There are three main types of cell division: binary fission, mitosis, and meiosis. Around two trillion cell divisions occur in the average human body every day! The centrosomes move to opposite ends of the nucleus to form the spindle poles. The process by which new cells are made is called cell division. Microtubules re-organise to form mitotic spindle. They make new cells in order to grow and also to replace old dead cells. Homologous chromosomes can exchange parts in a process called "crossing over.Living organisms are constantly making new cells. In Metaphase I, homologous chromosome pairs line up. This shuffling process is known as recombination or "crossing over" and occurs while the chromome pairs are lined up in Metaphase I. Each sibling is 50% mom and 50% dad, but which 50% of each can vary in the siblings. But this happens independently for each trait, so just because you got your dad's brown eyes doesn't mean you'll get his blond hair too. Each sperm and egg will end up with either B or b from mom and either B or b from dad. This leads to four possibilities: You could get B from mom and B from dad, or B from mom and b from dad, or b from mom and B from dad, or b from mom and b from dad. Imagine, for example, that eye color was controlled by a single gene, and that mom could have B, the allele for brown eyes or b, the allele for blue eyes, and dad could also have B or b. But each non-identical-twin child of these parents ends up with a different combination. You ended up with half of mom's paired genes and half of dad's paired genes. Your parents each have at least one pair of alleles (versions of a gene) for every trait (and many pairs of alleles for each polygenic trait).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
